Amazon Web Service (commonly known as AWS), a subsidiary of Amazon, is the world’s leading public cloud provider, catering to over a million active users worldwide. AWS provides you with on-demand cloud computing platforms on a pay-as-you-go model. AWS solutions are economical, scalable, and reliable, and are used by organizations of all sizes, including enterprises like AirBnB and GE.
Are you planning to deploy your applications on the AWS cloud? Read on to learn how you can simplify the process.
AWS Migration for your Business
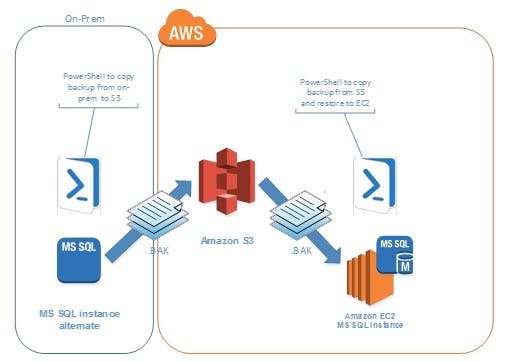
You can deploy your digital assets like data, applications, and other business elements, entirely or partially, to a cloud computing environment through a process called cloud migration.
One of the most common models of cloud migration is the transfer of data and applications from a local data center to a public cloud like AWS cloud.
Migration to AWS is not always as simple as ‘lifting and shifting’ applications (shallow cloud integration) from the on-premise data center to the AWS cloud. If you want a deep cloud integration to take advantage of cloud capabilities, you may have to modify certain applications.
You may face challenges, including issues with legacy application migration, data security, and regulatory compliance. You require significant planning and expertise for AWS migration to save time and costs and meet your business objectives.
Here is our 7 step process to migrate from an on-premise data center to AWS cloud:
Step 1- Preparation & Planning
Proper preparation and planning before migration help make the process simple and hassle-free.
Start by finding out which applications can be migrated to the AWS cloud easily and which ones would need modifications. Modify the application architecture to allow servers, networks, and data services to run and interact in the cloud computing environment. Plan how you will operate and run services on the cloud after completing the migration.
If you can not afford downtime for your users while migrating, formulate a strategy to transition without impacting them. Evaluate your security on a public cloud and plan your migration taking data security and regulatory compliance into account. Define cloud migration Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for your applications and services to track the progress and discover any issues.
Step 2- Discovery & Migration Approach
In this step. you start by collecting information about servers, applications, and data along with their inter-dependencies. Choose a discovery tool, like RISC, to track migration tasks and get more visibility into the migration progress. A discovery tool helps you gather information about the inter-dependence of the workloads by collecting server utilization data like configuration, usage, and behavior on your on-premise data center. Plan your data and application migration based on these dependencies.
Then, you finalize a migration approach for the applications. Below are the 6R’s of application migration- you can follow one of these approaches for each app:
Rehost: You simply ‘lift-and-shift’ the app from a local data center to cloud
Replatform: Here you lift the app, change the operating system or database version and move it to cloud- this also know as ‘lift-tinker-and-shift’ approach
Repurchase: You switch to a different application
Refactor/Re-architect: Following this approach, you change the middleware and app code to utilize cloud features for the application
Retire: You remove or ‘get-rid-of’ the app
Retain– You do nothing or keep the app as it is, usually until you can choose one of the other approaches- this may be a temporary arrangement as you may not want to keep many apps on the local data center
Step 3- Design
Design your cloud architecture based on your need for a public, private or hybrid cloud, and optimize your applications to run accordingly. Pick a tool to automate migration to AWS and set up for testing- automated or manual. Following this, plan for migration cutover. You can choose to continuously replicate data so that it is synced in real-time. This helps in reducing downtime during the cutover window.
Another essential thing to do is to have a rollback plan. In case you encounter an issue while migrating, have a step-wise roll back option to undo the last migration.
Step 4- Migrate
Your AWS migration can be very smooth depending on how well you have planned it as planning can help you minimize unexpected problems.
If you have smaller application and database sizes, you can copy them over the internet. For larger workloads, you may need to compress the data or use physical drives to transfer the data to the AWS cloud. Ensure that your sensitive data is secure during the migration by securing all temporary storage locations and end destination. Choose the right tools for migration. Match the new structure and limitations with your database. Track the application metadata to keep your application portable in the future.
Step 5- Validate
Test your applications and services to ensure smooth working. Evaluate if your apps and services work, and your data was migrated and it is accessible to the users. Check whether all the components are communicating and admin tools are monitoring the new cloud app. An automated testing strategy is ideal for these checks. Evaluate your performance against the cloud migration KPIs to determine the migration is successful.
Step 6- Operate
Decide whether you want to switch your production from the on-premise solution to the on-cloud solution by taking users all at once or in phases. Choose an approach based on the complexity and architecture of your apps, data, and data center.
You can:
Move the entire app to the cloud, validate that it works, and switch traffic to the cloud stack, or Shift a few customers at once and test the app until all the customers are on the cloud-based app.
Step 7- Optimize
Review the application resource allocation and optimization to take maximum advantage of the AWS cloud. Make a plan for the distribution of resources to your applications. You can allocate additional resources to an application in a cloud by getting in touch with AWS, scaling as per the demand.
Conclusion
AWS public cloud offers you many benefits for your business, including better productivity, operational resilience, and business agility. Migrating to AWS can be overwhelming, depending on the level of cloud integration and in-house expertise. That is where a cloud-managed service provider can help.